Q.1.Develop SRS as per IEEE standard for a Student Admission System.
A.1. SRS :-
1. Introduction:
The following subsections of the SRS document provide an overview of the entire SRS.
i) Purpose: The purpose of the project is to provide online facility to Institutes to conduct online exams and to Students to give online exams. Institutes can enter and edit the questions along with the students list. Also they can view the result. Students can login and give their respective exams and view their score then and there. Others can view sample papers to get look and feel of the online examination system.
ii) Scope: The website to conduct online Admission for a University is “Student Admission System”. This website provides facility to institutes to conduct online Admissions by providing a unique id to each Student. The institute provides online registration of the student. Institute also enters the list of eligible students. All the information entered can be later edited by the institute.
In turn student can login with their id, name and Programid to give the forms and can view their Admission status then and there. Institutes can also change the status of admission of their students (if needed).
Benefits: This website reduces the manual work, maintaining accuracy, increasing efficiency and saving time. Also institutes need not go to develop new software each time; instead they just register and admit the students online. For students, it saves time of going to far away admission centres and also they can view their Admission status then and there.
iii) Abbreviations:
JSP stands for Java Server Pages
HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol
iv) References:
IEEE Recommended Practice for Software Requirements Specification- IEEE STD 830-1993.
v) Overview: The rest of this SRS document describes the various system requirements, interfaces, features and functionalities in detail.
2. Overall Description: In Student Admission system institute can register to conduct an online admission and view the academic records later. Students can fill the form and their respective academic records (softcopy), which helps the registrar to admit the student or reject as per submited records. No student can take a particular online registration more than once.
i.) Product
Perspective:
(i) User interfaces
The application will have a user friendly and menu based interface.
Following screens will be provided:
(ii) A login screen for entering the username, password will be provided. Access to different screens will be based upon the user.
(iii) There is a screen for displaying information regarding entries to be made by institutes.
(iv) There is a screen for displaying information regarding filling of Admission form details by institutes.
(v) There is a screen for displaying information regarding entering student list for the particular program.
(vi) There is a screen for displaying information menu regarding what options the institutes will select while filling entries in the form.
(vii) There is a screen for displaying course details to the students when they are selecting program for admission.
(viii) There is a screen for submitted status for the students.
(ix) There is a screen for displaying of results of students after taking time for registrar for selecting and rejecting students in the selected list and rejected list.
(x) Hardware interfaces
(i) Support for printer for printing results then and there.
(ii) Screen resolution of at least 800X600 is required for proper and complete viewing of screens. Higher resolution will be accepted.
(xi) Software interfaces
(i) Any windows based operating system.
(ii) MS Access 2000 as the DBMS-for database.
(iii) IDE (NET BEANS) for developing code.
(xii) Communications interfaces None
(xiii) Memory Constraints At least 512 MB RAM and 5 MB space on hard disk will be required for running the application.
(xv) Site Adaptation Requirements Web browser with cookies enabled.
ii.) Product Functions: The website will allow access only to authorised users with specific roles (Administrator- maintains the website, Institutes-Register to select the forms submitted by the students, Students-Apply for admission online) a summary of the major functions that the website will perform:
a. Provide facility to institutes to register to conduct an student admission process.
b. Institutes can enter the number of programs and there course details and the list of eligible students selected.
c. Students can login and submit the admission form.
iii.) User Characteristics:
a. Educational level: Users should be comfortable with the English language.
b. Experience: Users should have prior information regarding the student admission process.
c. Skills: Users should have basic knowledge and should be comfortable using general purpose applications on computers.
iv.) Constraints:
* Since the DBMS being used is MS Access 2000, which is not a very popular DBMS, it will not be able to store a very huge number of records.
* Due to limited features of DBMS being used performance tuning features will not be applied to the queries and thus the system may become slow with the increase in number of records being stored.
* An extra security as SSL must be used to secure the marks details and other examination information.
v.) Assumptions: The application is online so taking into consideration that all the details are true. Students can submit application form just once.
vi.) Apportioning of Requirements: The future versions of the website will be having a better database to handle larger number of records, in a more secure way.
Also separate profile will be maintained later for all students so that he can view all his previous academic records later.
3. Specific Requirements: This section provides software requirements to a level of detail sufficient to enable designers to design the system and testers to test the system.
• External Interface Requirements:
* User Interfaces:
*Institute Registration Screen: Various fields available on this screen will be:
*Login Name
*Institute Name
*Email Id
*Password
*Institute Login Screen: Fields available on this screen are:
*Login Name
*Email Id
*Password
*Entering academic details: Various Fields are:
*Programs
*Course list for each Program
*Admission selected/rejected list Screen: Various Fields are:
*Student List Screen: Various Fields are:
*Student ID
*Student Name
*Student Login Screen: Various Fields are:
*Student ID
*Student Name
*Institute ID
*Result (Select/Reject)
*Hardware interfaces:
*Support for printer for printing results then and there.
*Screen resolution of at least 800X600 is required for proper and complete viewing of screens. Higher resolution will be accepted.
*Software interfaces:
*Any windows based operating system.
*MS Access 2000 as the DBMS-for database.
*IDE (NET BEANS) for developing code.
*Communications interfaces
None
ii.) Software Product Features:
Validity Checks: JavaScript provides validity checks for various fields in the forms.
Sequencing Information: All the information regarding exam details, student list, question details, display of result should be handled sequentially that is data should be stored only in a particular sequence to avoid any inconvenience
Error Handling: If any of the validations or sequencing flows does not hold true then
appropriate error messages will be prompted to the user for doing the needful.
iii.) Performance Requirements: This subsection specifies numerical requirements placed on the software or on the human interaction with the software, as a whole. Numerical requirements will include:
*300 terminals will be supported at a time
*Only text information will be supported (HTTP)
*All the transactions will be processed within seconds.
iv.) Design Constraints: None
v.) Software System Attributes:
*Security: Only authorized users will be able to access the website by entering the correct login name and corresponding password.
*Maintainability: The website can be maintained in present or future. It will be easy to incorporate new requirements in the individual modules.
*Portability: As the website is online so will be easily portable on various systems.
The website will be also easily portable on any windows based system that has MSACCESS installed.
*Logical Database Requirements: The following information will be placed in the database:
*Organization Details: ID, Login Name, Email, Password, Institute Name.
*Program Details: ID, Pname, No. of Course, No. of Duration, credits.
*Institute Student List: Sid, Sname, FormID, Result.
*Other Requirements: None
Q.2. Develop Design document for the system mentioned in Question 1.
A.2. ER Diagram :-
Notations for the components of ERD:Entities: An entity is something about which the business needs to store data. An entity is a class of persons, places, objects, events or concepts about which we need to capture and store data. An entity instance is a single occurrence of an
entity.
Attribute: An attribute is a descriptive property or characteristic of an entity. Synonyms include element, property and field.A compound attribute is one that actually consists of other attributes. It is also known as a composite attribute. An attribute “Address” is the example of compound attribute as shown in the following illustration
Relationships: A relationship is a natural business association that exists between one or more entities. The relationship may represent an event that links the entities.
Cardinality: defines the minimum and maximum number of occurrences of one entity that may be related to a single occurrence of the other entity. Because all relationships are bidirectional, cardinality must be defined in both directions for every relationship.
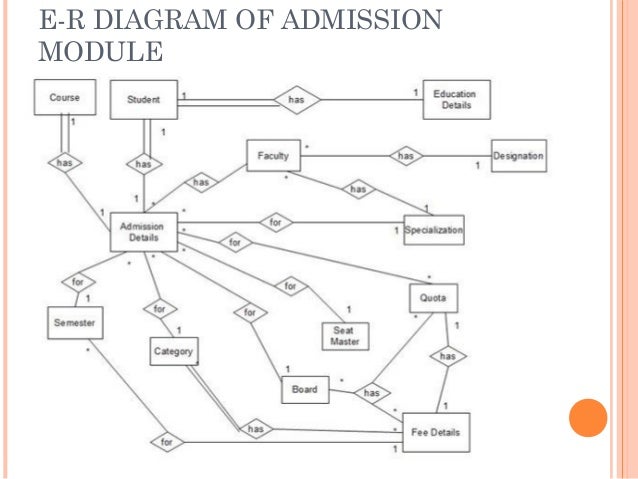
ERD for Student Examination System :-
A DFD can be categorized in the following forms:
ny system can be represented at any level of detail by these four symbols.
External Entities
External entities determine the system boundary. They are external to the system being studied. They are often beyond the area of influence of the developer.
These can represent another system or subsystem. These go on margins/edges of data flow diagram. External entities are named with appropriate name.
Processes
Processes are work or actions performed on incoming data flows to produce outgoing data flows. These show data transformation or change. Data coming into a process must be "worked on" or transformed in some way. Thus, all processes must have inputs and outputs. In some (rare) cases, data inputs or outputs will only be shown at more detailed levels of the diagrams. Each process in always "running" and ready to accept data.
Major functions of processes are computations and making decisions. Each process may have dramatically different timing: yearly, weekly, daily.
Naming Processes
Processes are named with one carefully chosen verb and an object of the verb. There is no subject. Name is not to include the word "process". Each process should represent one function or action. If there is an "and" in the name, you likely have more than one function (and process). For example, get invoice ,update customer and create Order Processes are numbered within the diagram as convenient. Levels of detail are shown by decimal notation. For example, top level process would be Process 14, next level of detail Processes 14.1-14.4, and next level with Processes 14.3.1-14.3.6. Processes should generally move from top to bottom and left to right.
Data Flow
Data flow represents the input (or output) of data to (or from) a process ("data in motion"). Data flows only data, not control. Represent the minimum essential data the process needs. Using only the minimum essential data reduces the dependence between processes. Data flows must begin and/or end at a process.
Data flows are always named. Name is not to include the word "data". Should be given unique names. Names should be some identifying noun. For example, order, payment, complaint.
Data Stores
or
Data Stores are repository for data that are temporarily or permanently recorded within the system. It is an "inventory" of data. These are common link between data and process models. Only processes may connect with data stores.
There can be two or more systems that share a data store. This can occur in the case of one system updating the data store, while the other system only accesses the data.
Context diagram:
An overview of an organizational system that shows the system boundaries, external entities that interact with the system and the major information flows between the entities and the system. In this diagram, a single process represents the whole system.
First level DFD:
A data flow diagram that represents a system’s major processes, data flows, and data stores at a high level of detail.
Q.3.What is Re-Engineering ? How does it differ from Reverse Engineering.
A.3.
Re-Engineering
Re-engineering is the investigation and redesign of individual components. It may also describe the entire overhaul of a device by taking the current design and improving certain aspects of it. The aims of re-engineering may be to improve a particular area of performance or functionality, reduce operational costs or add new elements to a current design. The methods used depend on the device but typically involve engineering drawings of the amendments followed by extensive testing of prototypes before production. The rights to re-engineer a product belong solely to the original owner of the design or relevant patent.
Reverse Engineering
Unlike re-engineering, reverse engineering takes a finished product with the aim of discovering how it works by testing it. Typically this is done by companies that seek to infiltrate a competitor's market or understand its new product. In doing so they can produce new products while allowing the original creator to pay all the development costs and take all the risks involved with creating a new product. Analysis of a product in this way is done without technical drawings or prior knowledge of how the device works, and the basic method used in reverse engineering begins by identifying the system's components, followed by an investigation into the relationship among these components.
Differences:
To reverse engineer a product is to examine it and probe it in order to reconstruct a plan from which it could be built, and the way it works. For instance if I took my clock apart, measured all the gears, and developed a plan for a clock, understanding how the gears meshed together, this would be reverse engineering.
Reverse engineering is often used by companies to copy and understand parts of a competitors product, which is illegal, to find out how their own products work in the event that the original plans were lost, in order to effect repair or alter them. Reverse engineering products is illegal under the laws of many countries, however it does happen. There have been celebrated cases of reverse engineering in the third world.
Re-engineering is the adjustment, alteration, or partial replacement of a product in order to change its function, adapting it to meet a new need.
For instance welding a dozer blade into the frame of my ford fiesta car is an example of re-engineering, in order to clear snow, or drive through my neighbors kitchen.
Re-engineering is often used by companies to adapt generic products for a specific environment (e.g. add suspension for rally car, change shape of conveyor belt to fit a factory shape, alter frequencies of a radio transmitter to fit a new countries laws).
No comments:
Post a Comment